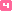
Alshafy 78 2017 이집트 RCT OP: CABG | CPB: ND 그룹 1(비타민 C): 50 그룹 2(대조군): 50 총계: 100
평균 연령: 그룹 1: 54.58±6.00 | 그룹 2: 55.88±5.37
♂: 그룹 1: 54% | 그룹 2: 60% |
IC: 허혈성 심장 질환으로 선택적 관상동맥 우회로술(CABG)을 시행, EF >30%, 1~4개 이식, 다른 심장 질환 없음, 허혈성 승모판 폐쇄 부전 없음.
EC: 이전에 관상동맥 우회로술을 시행, 응급 관상동맥 우회로술, EF <30% 환자, β-차단제 또는 AA에 대한 금기증 있음.
StR:
그룹 1: 수술 전 최소 3일 동안 비소프롤롤 5mg od & 비타민 C 2g 매일 qds.
그룹 2: 수술 전 최소 3일 동안 비소프롤롤 5mg od.
경로 ND.
OM: POAF, ICULOS, 환기 시간, 이노트로픽 수요 |
POAF(1일차 및 48시간 이후): 비타민 C: 5/50(10%) |대조군: 14/50(28%), P =0.022
POAF(1개월 후): 비타민 C: 2/50(4%) |대조군: 9/50(18%), P =0.025
퇴원 시 AF: SS, P =0.025
ICULOS(d): 비타민 C: 2.78±1.33 |대조군: 3.58±0.73, P =0.035
24시간 이상 환기 시간: 비타민 C: 14/50(28%) |대조군: 17/50(34%), P =0.048
수술 후 24시간 동안의 이노트로픽 수요: 비타민 C: 22/50(44%) | 대조군: 32/50(54%), P =0.045
합병증(신장, 신경, 출혈): NS. |
Angdin 79
2003 스웨덴 RCT DB OP: CS | CPB: 100%
그룹 1(치료): 12 그룹 2(위약): 10 그룹 3(대조군): 16 총계: 38
평균 연령: 그룹 1: 72 | 그룹 2: 66 | 그룹 3: 66
♂: 28/38 |
IC: 선택적 CS를 받는 성인, 수술 전 PVRI는 Ach 주입 후 5% 이상 감소.
EC: DM, 아세틸시스테인, 알로퓨리놀, 비타민 C 및 E로 치료.
StR:
그룹 1: 수술 전 10~14일 동안 매일 900mg VitE와 수술 전날 저녁에 2g Vit C 및 300mg 알로퓨리놀, 수술 당일 300mg VitE, 2g VitC 및 600mg 알로퓨리놀. 수술 중 수술 후 2시간까지 Ach 주입.
그룹 2: Ach만.
그룹 3: Ach 없음(식염수 제외).
OM: Ach 주입에 대한 폐 반응성 - 폐 혈관 저항 지수(PVRI), 산화 스트레스 마커(지질 과산화물, 총 항산화 활성, 디엔 접합체) |
ACH에 의해 유도된 PVRI 감소:
Ach는 치료군에서만 평균 폐동맥압을 감소시켰습니다.
지질 과산화물(pmol/mg 단백질):
치료: 수술 전: 5.16±1.24 | 수술 후: 16.69±2.15, P <0.0001
위약: 수술 전: 7.38±1.94 | 수술 후: 17.50±1.90, P <0.0001
총 항산화 활성(%):
치료: 수술 전: 37.6±0.7 | 수술 후: 31.5±1.6, P = 0.0007
위약: 수술 전: 36.9±0.9 | 수술 후: 30.1±0.9, P =0.0002.
항산화제를 투여받는 심장 환자의 경우 내피 의존성 혈관 확장이 수술 후 더 잘 유지되었습니다. |
Antonic 80
2016
슬로베니아
RCT
OP: CABG | CPB: 100%
AA: 52
대조군(표준 치료): 53
총계: 105
평균 연령: AA: 64.60±7.29 |대조군: 65.02±9.12
♂: AA: 80.8) |대조군: 75.5% |
IC: 선택적 온펌프 CABG 수술.
EC: 응급 수술, 동반 판막 또는 기타 수술, AF 병력, 영구적 심장 박동 조절기, 과옥살산뇨증 또는 신결석 병력, 오프펌프 수술.
StR:
수술 전: 2×2g: 수술 24시간 전 및 2시간 전 IV 수술
후: 5일간 2×1g/일 IV
β-차단제: AA: 수술 전 75.5 |대조군: 수술 전 78.8
아미오다론: AA: 수술 전 1.9 |대조군:
스타틴 전 1.9: AA: 수술 전 88.7 |대조군: 수술 전 92.3
OM: POAF, ICULOS, HLOS |
POAF: 비타민 C: 13.5% |대조군: 18.9%, P =0.314, NS
AF의 평균 지속 기간(시간): 비타민 C: 11.2±9.7 |대조군: 10.4±13.1, P =0.649
AF 발생 시간(POD): 비타민 C: 3.71±1.89 |대조군: 2.91±1.58, P =0.342
ICULOS(d): 비타민 C: 1.50±1.06 |대조군: 1.30±0.69, P =0.437
HLOS(d): 비타민 C: 9.37±.57 |대조군: 8.77±1.40, P =0.561.
이 연구의 결과는 선택적 온펌프 관상동맥 우회로술 환자의 POAF 발생률을 줄이는 데 있어 AA 보충의 효과를 뒷받침하지 않습니다. |
Antonic81
2017
Slovenia
RCT
OP: CABG | CPB: 100%
Vitamin C: 50
Control: 50
Total: 100
Mean age: 65.02 ± 9.12
♂: 78.1% |
IC: scheduled elective on-pump CABG
EC: severe preexistent acute or chronic kidney disease (NKF-K/DOQI) stages 4 & 5, eGFR <30 ml/min/1.73 m2, emergent surgery, critical preop state (Euro SCORE II), adjuvant valve surgery, exposure to contrast medium within 1-week preop, use of vitamin C within 1-month preop, off-pump surgery
StR:
Preop: 2×2 g 24 and 2 h before surgery IV
Postop: 2×1 g/day for 5 days IV
OM: POAF, ICULOS, HLOS, AEs, Postop AKI for 5 POD |
Postop AKI: VitC: 16% |Control: 14%, P=0.779
Postop serum Creat (µmol/l): VitC: 83 | Control: 83, P=0.434
ICULOS (d): VitC: 1.42±1.01 | Control: 1.38±0.75, P=0.902
HLOS (d): VitC: 9.32±2.52 | Control: 8.80±1.58, P=0.582.
NS protective effect of AA on the incidence of postop AKI.
Limitations: sample size was relatively small with only 100 patients included, short-term, (5 postop days), single-center trial. |
Bjordahl82
2012
USA
RCT TB
OP: CABG | CPB: 170/185
VitC: 89
Control (placebo): 96
Total: 185
Mean age: Vit C: 63±12.4 |Control: 63±12.4
♂: VitC: 68.5% |Control: 65.6% |
IC: >18 years old, undergoing nonemergency CABG.
EC: current AF, pacemaker, allergy to AA or any component of the trial supplement, pregnancy, emergency surgery, life expectancy <1-month, inability to take the trial AA supplement orally or by enteral tube.
StR:
Preop: 1×2 g PO night before surgery
Postop: 2×1 g/day PO or enteral tube for 5 postop days
b-blockers: AA: 82 pre | Control: 78.1 pre
OM: POAF, ICULOS, HLOS, AEs, Ventilator days, Vasopressor use, Death |
POAF: VitC: 27/89 –30.3% |Control: 29/96–30.2% P=0 .985
Ventilator time (d): VitC: 1.2±0.8 |Control: 1.4±1, P=0.032
ICULOS (d): VitC: 3.7±2.2|Control: 4.3±2.9, P=0.155
HLOS (d): VitC: 10.4±4 |Control: 11.7±7.1, P=0.124
Mortality: VitC: 2/89–2.2% |Control: 4/94–4.2%, P=0.836
Supplementation of AA in addition to routine postop care does not reduce AF after CABG |
Carnes83
2001
USA
Pilot retrospective
OP: CABG | CPB: ND
VitC: 43
Control: 43
Total 86
Mean age: VitC: 61.6±12.2 |Control: 61.8±11.2
♂: VitC: 83.7% |Control: 83.7% |
IC: scheduled for primary CABG.
EC: abnormal renal dysfunction not in sinus rhythm (preop AF).
StR:
Preop: 1×2 g VitC PO the night before surgery
Postop: 2×500 mg PO for 5 days after surgery
b-blockers: AA: 86 pre, 84 post | Control: 76 pre, 70 post.
OM: POAF or atrial flutter for 5 POD. |
POAF: VitC: 7/43–16.3%| Control: 17/43– 34.9%, P=0.048
B-blocker use has the most protective effect (84% risk reduction, P=0.007) and suggests that AA usage alone (66% risk reduction, P=0.09) would also have a clear beneficial effect.
Weakness: not all risk factors were matched between groups as the incidences of hypertension, diabetes and prior AF were higher in the control group. Patients not blinded to treatment. No consistency in length of postop treatment with AA |
Castillio49
2010
Chile
RCT DB
OP: CS | CPB: 100%
VitC: 48
Control: 47
N=95
Mean age: 59 years
♂: 68/95 |
IC: elective on-pump surgery, sinus rhythm.
EC: AF, congenital or previous heart surgery, cirrhosis, chronic renal failure (Cr>150lM), inflammatory or rheumatic diseases, corticosteroid users, use of anti-inflammatory or antioxidant actions, use fish oil supplements 3 months previously.
StR:
N-3 PUFAs 2 g/day for 7 days before, VitC 1 g/day & Vit E 400 IU/day from 2 days before surgery all until discharge.
OM: POAF, GSH ⁄ GSSG, MDA, Protein carbonylation, Leukocyte count, high sensitivity (hs) -CRP, Nuclear factor (NF) - kappa B activation |
POAF: VitC: 11/48–22.9% | Control: 15/47 – 31.9%, P=0.32
HLOS (d): VitC: 8.15±0.16 |Control: 9.20±0.18, P=0.02
Lipid peroxidation (MDA) and Protein carbonylation were 27.5% and 24% lower in supplemented patients (P<0.01).
Leukocyte count and serum hs-CRP levels were markedly lower throughout the protocol in supplemented patients (P<0.01).
The combined n-3 PUFAs-antioxidant vitamin protocol therapy reduced the oxidative stress and inflammation biomarkers, in patients undergoing on-pump CS |
Colby84
2011
USA
RCT DB
OP: CS | CPB: 50%
VitC: 13
Control (placebo): 11
Total: 24
Mean age: 65.5 ± 8.8
♂: 79% |
IC: >18 years old, undergoing CABG±valve surgery.
EC: pregnant, history of renal calculi, hypersensitivity to AA
StR:
Preop: 1×2 g PO night before
Postop: 2×0.5 g/day PO the day of surgery to postop 4th day
b-blockers: AA: 54 pre, 85 post |Control: 55 pre, 100 post
Amiodarone: AA: 36 post |Control: 27 post
Statins: AA: 77 pre, 77 post | Control: 73 pre, 91 post
OM: POAF, ICULOS, HLOS, AEs, Inflammatory mediators (CRP, WBC, Fibrinogen). |
POAF: VitC: 31% |Control: 45%, P=0.498, NS
ICULOS (h): VitC: 106.4±249.9|Control: 48.9±43.2, P=0.461
HLOS (days): VitC: 14.6±17.6 |Control: 10.2±4.9, P=0.429
[CRP] (mg/dl): PO4
Vit C: 14.5±7.8 | Control: 20.4±9.7
On-pump: 16.8±5.9| Off-pump: 17.8±11.5
WBC count (1000 cells/mm): POD4
Vit C: 9.4±3.1 | Control: 9.7±3.0
On-pump: 9.9±2.8| Off-pump: 8.8±3.3
Fibrinogen (mg/dl): POD4
Vit C: 673.9±190.1| Control: 684.6±239.7
On-pump: 680.4±204.6| Off-pump: 667.4±183.4 |
Das85 2016 India RCT D
OP: CS | CPB: 100%
VitC: 35 Control (placebo): 35 Total: 70
Mean age: VitC: 48.14±6.46|Control: 45.23±11.47
♂: ND |
IC: free of any endocrine disease, aged 25–60 years old, NYHA status <IV, scheduled for elective CS.
EC: parsonnet score >10, use of steroids, DM, alcohol abuse, smokers, pregnancy, epilepsy, hematological disease, impaired hepatic or renal function, hypersensitivity to any of the study drugs, requiring cross clamp time >2 h.
StR:
Preop: 2×0.5 g VitC po for 7 days prior to surgery till morning of surgery.
OM: Cortisol level |
Cortisol level 1st postinduction h: VitC: 69.51±7.65| Control: 27.74±4.72, P<0.05
Vasopressor demand: VitC: 2.83±1.27 | Control: 3.40±1.09, P=0.047.
Time of extubation, ICULOS, incidence of arrhythmias was similar in both the groups.
Adrenal suppression by etomidate was statistically significantly less in Vit c as compared to control group which is reflected by a higher level of cortisol in patients who received VitC |
Dehghani86
2014
Iran
RCT
OP: CABG | CPB: 100%
VitC: 50
Control (no vitC): 50
Total: 100
Mean age: 61.31±6.42
♂: 74% |
IC: >50 years old, without history of CABG surgery, taking b-blocker, undergoing elective isolated on-pump CABG.
EC: arrhythmia: using AADs or digoxin, severe chronic HF, LV EF<30%, pacemaker, renal (Cr>1.5) or hepatic failure, COPD, no occurrence of intra- or post-operative cardiopulmonary arrest, any degree of cardiac blockade, bradycardia <50 bpm.
StR:
Preop: 1×2 g Vit PO
Postop: 2×0.5 g (500 mg) /day for 5 days PO
B -blockers: all patients 1 wk before and continued postop
Statins: AA: 18 pre, 14 post | Control: 20 pre, 16 post
OM: POAF, ICULOS, HLOS, AEs |
POAF: VitC: 4/50–8% | Control: 16/50–32%, P=0.003
Length of POAF (d): VitC: 2±0.816 | Control: 2.69±1.195, P=0.295
Time needed for converting AF to SR (h): VitC: 3.37±1.03| Control: 14±28.95, P=0.395
ICULOS (d): VitC 1.79±0.313 |Ctrl 2.10±0.61, P=0.002
ICULOS (d): AF: 1.80±0.30 |no AF: 2.56±0.69, P=0.001
HLOS (d): VitC 5.32±0.59 | Ctrl 5.74±1.3, P=0.041
HLOS (d): AF: 5.25±0.50 |no AF: 6.65±1.70, P=0.001
Ventilation time (h): VitC: 13.38±2.01 | Control: 15.41±14.35, P=0.325 |
Dingchao43
1994
China
RCT
OP: CABG | CPB: 100%
VitC: 45
Control: 40
Total: 85
Mean age: ND
♂: ND |
IC: ND
EC: ND
StR:
2×125 mg/kg: 30 min before surgery and at the end of CPB (after aortic declamping) IV.
Totally: 250 mg/kg
OM: MDA, CPK, CPK-MB, LDH |
Changes in serum MDA, CPK, CPK-MB, LDH in group of VitC were lower (P<0.05) than in control during and after CPB.
CPK: VitC: 45/45 (100%) |Control: 35/40 (87.30%), P<0.05
ICULOS (h): VitC: 25±4.7 |Control: 45±8.5, P<0.05
HLOS (d): VitC: 35±5.9 | Control: 35±5.9, P<0.05 |
Eslami87
2007
Iran
RCT - No blinding
OP: CABG | CPB: 100%
VitC: 50
Control (no AA): 50
Total: 100
Mean age: 60.19±7.14
♂: 67% |
IC: >50 years old, taking b-blocker at least 1-week preop (for a target HR 60–70 bpm), scheduled for elective CABG.
EC: history of AF, class I or III AAD or digoxin, pacemaker, AV block, bradycardia (HR <50 bpm), hepatic disease, end stage renal disease, severe pulmonary disease (pneumonia or COPD), severe hepatic disease (cirrhosis or fulminant hepatitis).
StR:
Preop: 2 g the night before surgery PO
Postop: 2×1 g for 5 days PO.
All patients received b-blockers for at least 1-week preop and continued postop.
OM: POAF for 4 POD, ICULOS, HLOS, AEs |
POAF: VitC: 2/50–4%|Control: 13/50–26%, P=0.002, OR 0.119, 95% CI: 0.025–0.558
ICULOS (h): VitC 55.2+/-38.4 |Ctrl 62.4+/-35.5, NS
HLOS (d): VitC 6.54 (6.5) (+/-3.24 (3.2) | Ctrl 7.08 (7.0)+/-3.45
HLOS (d): AF: 8.9±3.9 |no AF: 6.5±3.1, P=0.02
ICULOS (d): AF: 3.23±1.92|no AF: 2.33±1.45, P=0.09.
Combination of AA and b-blockers may be more effective in reducing POAF than b-blockers alone |
Gholami25
2019
Iran
RCT TB
OP: CABG | CPB: 100%
Intervention: 80
Control (placebo): 80
Total: 160
Mean age: VitC: 61.41±10.51 | Control: 63.93±9.97
♂: VitC: 55% | Control: 47.5% |
IC: ≥18 years old, no prior use of antioxidants, no use of fish oil over the past 3 months, lack of diseases with high inflammatory components.
EC: hypersensitivity to n-3 PUFAs or Vit C, developing heart attack during or following the surgery.
StR:
Preop: n-3 PUFAs 2 g/bid & Vit C 1 g/bid the day before.
Post: 2 g n-3 PUFAs (1 g/bid) and 1 g VitC (500 mg/bid) until the 5th postop day.
OM: Fatigue - MFI-20 scale |
Fatigue score: Intervention: 62.01±4.06 | Control: 67.92±4.95, P<0.0001.
Changes in general fatigue score: VitC: 1.42±1.15 | Control: 2.66±2.50.
Changes in physical fatigue score: VitC: 1.99 0.23 |Control: 2.26±1.53, P<0.0001.
Changes in reduced active score: VitC: 1.83±0.14| Control: 1.83±0.14, P=0.01.
Changes in mental fatigue score: VitC: 3.00±2.16| Control: 3.32±2.44, P=0.586, NS
Combination of vitamin C and n-3 PUFAs effectively reduces postop fatigue among patients who undergo CABG surgery |
Gunes88 2012 Turkey Retrospective
OP: CS | CPB: 100%
Intervention: 34 Control: 25 Total: 59
Mean age: Intervention: 57.29±2.50 | Control: 55.08±2.87
♂: 45/59 |
IC: ND
EC: ND
StR:
Preop: VitC 500 mg and VitE 300 mg on the day of surgery IV
Postop: VitC 500 mg/day and VitE 300 mg/day for 4 days IV
All patients received 500 mg of methylprednisolone (in CPB).
OM: CRP, WBC count, serum lipids (HDL, LDL, triglycerides) |
Control group:
CRP ↑ POD1 (P<0.001)
CRP+r with triglycerides D0 (P=0.009) and POD1 (P=0.021)
WBC ↓POD2 (P=0.008)
WBC+r with glucose POD2 (P<0.005)
Study group:
CRP -r with HDL (P=0.049) on POD1
CRP +r with triglycerides on the POD2 (P=0.017)
Blood Glucose ↑ POD1 (P=0.021)
WBC +r with VitC and VitE on the POD4 (P=0.027)
VitC and VitE seem to display some anti-inflammatory effect |
Jouybar89
2012
Iran
RCT
OP: CABG | CPB: 100%
Vit C: 20
Control (placebo): 20
Total: 40
Mean age: VitC: 56.9±10.3 | Control: 61.83±10.45
♂: VitC: 14/20 | Control: 12/20 |
IC: scheduled elective CABG, ASA score I or II
EC: pregnancy, infection, malignant disease, history of hypersensitivity reaction, hematologic disease or abnormal WBC, DM, major trauma or major surgery <6 m preop, EF<35%, use of immunosuppressive drugs, uncontrolled BP, recent myocardial infarction <6 m, renal failure.
StR:
Preop: 2×3 g 12–18 h preop and during CPB initiation (after induction of anesthesia)
OM: Inflammatory markers (IL6 and IL8) |
IL6 and IL8 increased significantly after starting CPB. The pattern of changes at such levels was similar in both groups.
AA has no effect on the reduction of inflammatory cytokines (IL6 and IL8) during CPB and did not improve kidney function. It causes no improvement in hemodynamics (P=0.37), blood gas variables (P=0.21), and the outcomes of patients undergoing CABG |
Knodell90
1981
USA
RCT DB
OP: CS | CBP: ND
VitC: 111
Control (placebo): 104
Total: 215
Mean age: VitC: 53.6±8.8 | Control: 54.1±9.9
♂: ND |
IC: scheduled CABG
EC: ND
StR:
Preop: 4×800 mg/day VitC PO for 2 days before surgery
Postop: 4×800 mg/day VitC PO for 2 weeks postop started as soon as patient could take oral liquids
OM: Posttransfusion hepatitis (liver enzymes) |
Posttransfusion hepatitis: VitC: 6.7% | Control: 9.4%, P>0.50. significant elevations of plasma VitC in VitC treatment group, P<0.0005.
Elevations of plasma VitC no influence on the hepatitis |
Papoulidis91
2011 Greece RCT DB
OP: CABG | CPB: 100
VitC: 85 Control (placebo): 85 Total: 170
Mean age: VitC: 73.1±7.2 |Control: 71.3±6.8
♂: VitC: 67% | Control: 74.1% |
IC: >65 years old, NYHA Class III or IV HF, taking b-blocker, scheduled for elective isolated CABG.
EC: age <65, preop AF, hyperoxaluria, permanent or temporary pacemaker, severe renal or hepatic failure, medication with class I and III AAD or digoxin, any degree of AV or bradycardia (HR <50 bpm), severe pulmonary disease (pneumonia or COPD).
StR:
Preop: 1×2 g 3 h prior to CPB IV
Postop: 2×0.5 mg/day for 5 days IV
All patients (100%) were on b-blockers both preop and postop.
OM: POAF for 5 POD, HLOS, AEs |
POAF: VitC: 38/85 (44.7%) | Ctrl: 52/85 (61.2%), P=0.041.
Time needed for cardioversion in AF patients (h): VitC: 5±1.3 h | Control: 7.3±2.1, P=0.047
HLOS (d): AF: 9.5±2.8 | no AF: 6.7±1.9, P=0.034
HLOS (d): VitC: 7.9±2.2 |Control: 9.8±3.6, P=0.04
ICULOS (d): VitC: 1.6±0.9 | Control: 2.1±1.1, P=0.05
Combination of AA and b-blockers reduced the incidence of POAF |
Sadeghpour39 2015 Iran RCT
OP: CS (CABG, Valve, Congenital) | CPB: 249/290
VitC: 113 Control (placebo): 177 Total: 290
Mean age: 55.78±13.72
♂: VitC: 70.8% | Control: 62.7% |
IC: ≥18 years old, undergoing CS, ASA II-III
EC: severe cardiac, respiratory, or neurologic complications, emergency surgery, death on postop day 1, those who had not received adequate doses of drugs according to protocol.
StR:
Preop: 1×2 g immediately before surgery (at operating room) IV
Postop: 1×1 g/day for 4 days postop PO
OM: POAF, ICULOS, HLOS, AEs |
POAF: VitC: 40/113 (35.3%) |Control: 99/177 (55.9%), P = 0.001
HLOS (d): VitC: 10.17±4.63|Control: 12±4.51, P=0.01
Intubation time (h): VitC: 11.83±3.91 |Control: 14.14±9.52, P=0.003
Drainage volume the 1st 24 h postop (cc): VitC: 262.21±190.91 |Control: 348.50±262.17, P=0.003.
Postop complications: Significant difference, P=0.042.
This trial suggests benefit from the routine early, prophylactic administration of VitC |
Safaei92 2017 Iran RCT
OP: CABG |CPB: 100%
Group 1 (no treatment): 29 Group 2: 29 Group 3: 29 Total: 8
Mean age: 57.07±1.05
♂: 67/87 |
IC: elective isolated CABG
EC: urgent patients, complicated high-risk patients, DM, another heart surgery beside CABG, ischemic time >120 min
StR:
Group 2: 4×100 mg Grape Seed Extract (GSE) 24 h before operation PO
Group 3:25 mg/kg vitamin C during surgery iv
OM: Total Antioxidant Capacity (TAC), Malondialdehyde (MDA), Superoxide Dismutase (SOD), Glutathione Peroxidase (Gpx) |
ICULOS (h): VitC: 67.0±3.0| Control: 71.2±6.1, P=0.61
Tracheal intubation time (h): VitC: 15.1±1.0 | Control: 22.9±3.8, P=0.019
TAC: was higher (P<0.05) in both grape seed and VitC groups at T2 (ischemic period) and T3 times (Post-I/R period).
MDA: in both GSE and VitC groups were always lower compared to control.
GSE and VitC had antioxidative effects and reduced deleterious effects of CPB. No hospital mortality or AE occurred in study groups |
Samadikhah93
2014
Iran
RCT DB
OP: CS | CPB: ND
VitC: 60
Control (placebo): 60
Total: 120
Mean age: VitC: 61.0±11.5 |Control: 60.5±11.3
♂: VitC: 43/60 | Control: 39/60 |
IC: patients undergoing CABG
EC: history of AF, valve disease, MI, EF <40%, LAH, heart valve disease, myocardial infarction
StR:
Preop: 1×2 g PO
Postop: 1×1 g/day PO from 2nd until 5th POD
Atorvastatin (for both groups): 40 mg PO until 5th postop day.
b-blockers: AA: 75 pre | Control: 66 pre
Statins: AA: 98.3 pre, 100 post | Control: 98.3 pre, 100 post
OM: POAF |
POAF: VitC: 6/60–10% | Control: 15/60–25%, P=0.03, OR=0.33, 95% CI=0.12–0.93
Combination prophylaxis against POAF with oral atorvastatin plus VitC is significantly more effective than single oral atorvastatin |
Sisto94
1995
Finland
RCT
OP: CABG | CPB: 100%
Stable or Low risk:
VitC: 20 | Control: 25
Unstable or High-risk:
VitC: 17 | Control: 19
Total: 81
Mean age: Group 1: 54 ±8 | Group 2: 58±6 | Group 3: 55±8 | Group 4: 62±6
♂: 56/81 |
IC: undergoing standard CABG.
EC: women of premenopausal age, MI, use of study medicines during 30 days before CABG, renal (Cr >150 ~g/l) or hepatic (AST >40 IU/l) disease, allergy to study medicines.
StR:
Stable or low risk disease:
Preop: 600 mg daily VitE for 4 weeks preop, 2 g daily VitC for 2 days before, 600 mg daily allopurinol for 2 days before PO
Postop: 2 g daily VitC, 600 mg daily allopurinol for 1-day postop PO
Unstable or high-risk:
Preop: 600 mg daily VitE, 2 g daily VitC, 600 mg daily allopurinol for 2 days before PO
Postop: 2 g daily VitC, 600 mg daily allopurinol for 1-day postop PO
OM: Arrhythmias (AF) for 5 POD, CK-MB |
Incidence of arrhythmias:
High-risk patients: VitC: 12% | Control: 42%, P=0.05
Lower-risk patients: VitC: 25% | Control: 24%, P=ND
ECG ischemic events:
Low risk: VitC: 20% | Control: 52%, P=0.03
High-risk: VitC: 18% | Control: 58%, P=0.01
Postop MI:
Low risk: VitC: 5% | Control: 8%, P=ND
High-risk: VitC: 6% | Control: 32%, P=0.06
CK-MB release: lower in groups treated with antioxidants and allopurinol than in the controls.
Vasopressor demand: control groups tended to require more dopamine than treatment groups (P=0.057).
Combination therapy with allopurinol, vitamin C, and vitamin E appeared to inhibit ischemic ECG alterations and may protect against post-CABG arrhythmias |
Stanger95
2014 Australia RCT DB
OP: CABG | CPB: ND
Group 1 – Control: 20 Group 2 – Vitamins: 19 Group 3 – n-3 PUFAs: 19 Group 4 – Vitamins & n-3 PUFAs: 17 Total: 75
Mean age: 66±8
♂: 68/75 |
IC: good pharmacological control, lipid profile, blood pressure values and glycemic control
EC: ND
StR:
Group 1: Control (C)
Group 2:500 mg VitC & 45IE VitE IV 30 m before reperfusion and 120 m after reperfusion
Group 3:2×0.15 g fish oil/kg 42 h and 18 h before surgery and 50 ml 42 h after surgery IV
Group 4: 2×0.15 g fish oil/kg 42 h and 18 h before surgery and 50 ml 42 h after surgery IV plus 500 mg vitC and 45IE vitE IV 30 m before reperfusion and 120 m after reperfusion
OM: Serum oxidative stress biomarkers: Total peroxides, Endogenous peroxidase activity, Antibodies against oxidized LDL (oLAb) |
POAF: Group 2: 5/19| Group3: 4/19| Group 4: 7/17
Vitamin supplementation was associated with a significant decrease in total peroxides both in Vit as well as in Vit & n-3 PUFAs, compared to C and n-3 PUFAs.
Olab: significantly decreased only in C (P=0.002) at the POD1.
Water-soluble and Lipid-soluble antioxidants: significantly decreased at the 1st and 2nd postop days in all subgroups but recovered at the 3rd postop day.
Postop increase in oxidative stress was associated with the consumption of antioxidants and a simultaneous onset of AF. The administration of vitamins attenuates postop oxidative stress during CABG. In both subgroups that were supplemented with vitamins, total peroxides decreased |
Rodrigo96
2012 Chile RCT DB OP: CS | CPB: 100%
VitC: 77 Control (Placebo): 75 Total: 152
Mean age >60: VitC: 66 |Control: 65 Mean age <60: VitC: 53 |Control: 52
♂: VitC: 59/77 | Control: 61/75 |
IC: scheduled CS with extracorporeal circulation.
EC: previous CS, chronic or paroxysmal AF, other preop arrhythmias, advanced pulmonary or hepatic disease, chronic renal failure (serum creatinine >2.0 mg/dl).
StR:
2 g/d n-3 PUFAs 7 days before surgery and Vit C (1 g/day) and Vit E (400 IU/day) 2 days before and all continued until the discharge from hospital.
OM: POAF until hospital discharge, Activity of antioxidant enzymes: Cu-Zn superoxide dismutase, catalase and GSH-Px activities, Plasma MDA |
POAF:
Patients <60 years old: VitC: 5/40–12.5% |Control: 12/40–30%
Patients >60 years: VitC: 2/37–5.4% |Control: 10/35–2.8.5%, P=0.0076
Patients >60 years present higher levels of lipid peroxidation, lower enzymatic activity of GSH-Px and decreased total antioxidant plasma capacity.
Patients with POAF showed higher plasma MDA levels postop and lower atrial GSH-px activity compared with those who did not present POAF (P<0.01).
Antioxidant supplementation resulted in a more marked reduction of POAF in older patients. It could be suggested that the efficacy of this therapy improves with ageing |
Rodrigo97
2013
USA
RCT DB
OP: CS |CPB: 100%
Intervention: 103 Control (Placebo): 100 Total: 203
Mean age: VitC: 61| Control: 58.5
♂: VitC: 85| Control: 88 |
IC: ≥18 years old, scheduled for CABG or/and valve surgery, sinus rhythm.
EC: history of any arrhythmia, previous MI, use of amiodarone or sotalol, severe CHF (NYHA III or IV), prosthetic valves, congenital valvular disease, left atrial diameter >50 mm, conditions associated with oxidative stress or inflammation such as chronic rheumatic or neoplastic diseases, liver insufficiency, severe chronic kidney disease (serum Cr >2.0 mg/dl), recent infections, use of NSAID, corticosteroids, antioxidant vitamins, or fish oil supplements 3 m preop.
StR:
N-3 PUFAs 2 g/day 7 days prior to surgery and 2 days before surgery added VitC 1 g/day and VitE 400 IU/day until discharge.
OM: POAF, Biomarkers of oxidative stress and inflammation |
POAF: Intervention: 10/13–9.7%| Control: 32/100–32%, P<0.001, RR: 0.28, 95% CI: 0.14– 0.56
Duration of POAF (h): VitC: 10.8±0.7 |Control: 11.2±1.5, P=0.06
ICULOS (d): VitC: 2.87±0.44| Control: 3.08±0.54 P=0.76
HLOS (d): VitC: 8.77±0.37|Control: 9.57±0.66 P<0.05.
The activity of catalase, superoxide dismutase, and glutathione peroxidase in atrial tissue of the supplemented patients was 24.0%, 17.1%, and 19.7% higher than the respective placebo values (P<0.05).
The atrial tissue of patients who developed AF showed NADPH oxidase p47-phox subunit protein and mRNA expression 38.4 and 35.7% higher, respectively, than patients in SR (P<0.05) |
Westhuyzen98
1997
Australia
RCT DP
OP: CABG | CPB: 100%
Intervention: 38
Control (placebo): 38
Total=76
Mean age: 59.7±7.3
♂: 82.9% |
IC: elective CABG, aged 18–75, no smokers, gave informed consent >10 days preop.
EC: receiving coumarin derivatives, vitamin supplements, corticosteroids, malabsorption syndrome, severe asthma, COPD, EF<40%, history of alcoholism, drug abuse, psychosis.
StR:
750 IU VitE/day PO for 7 to 10 days prior to surgery and 1 g VitC PO 12 h before the operation.
OM: CK-MB, Plasma a-tocopherol, Myocardial injury (ECG, SPECT) |
Plasma [a-tocopherol] (mg/l):
Preop: raised fourfold by supplementation. Intervention: 44.7% |Control: 11.4, P<0.001.
Postop: fell by 70% in the supplemented group and to negligible levels in placebo group.
CK-MB profiles: NS differences, P=0.71
ECG:
Preop: The treatment group had significantly worse QRS scores than the placebo group at baseline (P=0.03).
Postop: QRS scores were worse than preop scores in the combined group (P=0.001).
SPECT: NS differences |